JDBC Interview Questions
A list of top frequently asked JDBC interview questions and answers is given below.1) What is JDBC?
JDBC is a Java API that is used to connect and execute the query to the database. JDBC API uses JDBC drivers to connect to the database. JDBC API can be used to access tabular data stored into any relational database.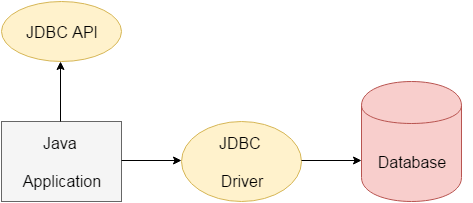 More details.
More details.
2) What is JDBC Driver?
JDBC Driver is a software component that enables Java application to interact with the database. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:- JDBC-ODBC bridge driver: The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver uses the ODBC driver to connect to the database. The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver converts JDBC method calls into the ODBC function calls. This is now discouraged because of the thin driver. It is easy to use and can be easily connected to any database.
- Native-API driver (partially java driver): The Native API driver uses the client-side libraries of the database. The driver converts JDBC method calls into native calls of the database API. It is not written entirely in Java. Its performance is better than JDBC-ODBC bridge driver. However, the native driver must be installed on each client machine.
- Network Protocol driver (fully java driver): The Network Protocol driver uses middleware (application server) that converts JDBC calls directly or indirectly into the vendor-specific database protocol. It is entirely written in Java. There is no requirement of the client-side library because of the application server that can perform many tasks like auditing, load balancing, logging, etc.
- Thin driver (fully java driver): The thin driver converts JDBC calls directly into the vendor-specific database protocol. That is why it is known as the thin driver. It is entirely written in Java language. Its performance is better than all other drivers however these drivers depend upon the database.
3) What are the steps to connect to the database in java?
- Registering the driver class: The forName() method of the Class class is used to register the driver class. This method is used to load the driver class dynamically. Consider the following example to register OracleDriver class.
- Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- Creating connection: The getConnection() method of DriverManager class is used to establish the connection with the database. The syntax of the getConnection() method is given below.
- 1) public static Connection getConnection(String url)throws SQLException
- 2) public static Connection getConnection(String url,String name,String password)
- throws SQLException
- Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(
- "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","password");
- Creating the statement: The createStatement() method of Connection interface is used to create the Statement. The object of the Statement is responsible for executing queries with the database.
- public Statement createStatement()throws SQLException
- Statement stmt=con.createStatement();
- Executing the queries: The executeQuery() method of Statement interface is used to execute queries to the database. This method returns the object of ResultSet that can be used to get all the records of a table.
- public ResultSet executeQuery(String sql)throws SQLException
- ResultSet rs=stmt.executeQuery("select * from emp");
- while(rs.next()){
- System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)+" "+rs.getString(2));
- }
- Closing connection: By closing connection, object statement and ResultSet will be closed automatically. The close() method of Connection interface is used to close the connection.
- public void close()throws SQLException
- con.close();
Syntax of executeQuery() method is given below.
Syntax of close() method is given below.
4) What are the JDBC API components?
The java.sql package contains following interfaces and classes for JDBC API.Interfaces:
- Connection: The Connection object is created by using getConnection() method of DriverManager class. DriverManager is the factory for connection.
- Statement: The Statement object is created by using createStatement() method of Connection class. The Connection interface is the factory for Statement.
- PreparedStatement: The PrepareStatement object is created by using prepareStatement() method of Connection class. It is used to execute the parameterized query.
- ResultSet: The object of ResultSet maintains a cursor pointing to a row of a table. Initially, cursor points before the first row. The executeQuery() method of Statement interface returns the ResultSet object.
- ResultSetMetaData: The object of ResultSetMetaData interface cotains the information about the data (table) such as numer of columns, column name, column type, etc. The getMetaData() method of ResultSet returns the object of ResultSetMetaData.
- DatabaseMetaData: DatabaseMetaData interface provides methods to get metadata of a database such as the database product name, database product version, driver name, name of the total number of tables, the name of the total number of views, etc. The getMetaData() method of Connection interface returns the object of DatabaseMetaData.
- CallableStatement: CallableStatement interface is used to call the stored procedures and functions. We can have business logic on the database through the use of stored procedures and functions that will make the performance better because these are precompiled. The prepareCall() method of Connection interface returns the instance of CallableStatement.
- DriverManager: The DriverManager class acts as an interface between the user and drivers. It keeps track of the drivers that are available and handles establishing a connection between a database and the appropriate driver. It contains several methods to keep the interaction between the user and drivers.
- Blob: Blob stands for the binary large object. It represents a collection of binary data stored as a single entity in the database management system.
- Clob: Clob stands for Character large object. It is a data type that is used by various database management systems to store character files. It is similar to Blob except for the difference that BLOB represent binary data such as images, audio and video files, etc. whereas Clob represents character stream data such as character files, etc.
- SQLException It is an Exception class which provides information on database access errors.
5) What are the JDBC statements?
There is three type of JDBC statements given in the following table.
| Statements | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Statement | Statement is the factory for resultset. It is used for general purpose access to the database. It executes a static SQL query at runtime. |
| PreparedStatement | The PreparedStatement is used when we need to provide input parameters to the query at runtime. |
| CallableStatement | CallableStatement is used when we need to access the database stored procedures. It can also accept runtime parameters. |
6) What is the return type of Class.forName() method?
The Class.forName() method returns the object of java.lang.Class object.7) What are the differences between Statement and PreparedStatement interface?
| Statement | PreparedStatement |
|---|---|
| The Statement interface provides methods to execute queries with the database. The statement interface is a factory of ResultSet; i.e., it provides the factory method to get the object of ResultSet. | The PreparedStatement interface is a subinterface of Statement. It is used to execute the parameterized query. |
| In the case of Statement, the query is compiled each time we run the program. | In the case of PreparedStatement, the query is compiled only once. |
| The Statement is mainly used in the case when we need to run the static query at runtime. | PreparedStatement is used when we need to provide input parameters to the query at runtime. |
8) How can we set null value in JDBC PreparedStatement?
By using setNull() method of PreparedStatement interface, we can set the null value to an index. The syntax of the method is given below.- void setNull(int parameterIndex, int sqlType) throws SQLException
9) What are the benefits of PreparedStatement over Statement?
The benefits of using PreparedStatement over Statement interface is given below.- The PreparedStatement performs faster as compare to Statement because the Statement needs to be compiled everytime we run the code whereas the PreparedStatement compiled once and then execute only on runtime.
- PreparedStatement can execute Parameterized query whereas Statement can only run static queries.
- The query used in PreparedStatement is appeared to be similar every time. Therefore, the database can reuse the previous access plan whereas, Statement inline the parameters into the String, therefore, the query doesn't appear to be same everytime which prevents cache reusage.
10) What are the differences between execute, executeQuery, and executeUpdate?
| execute | executeQuery | executeUpdate |
|---|---|---|
| The execute method can be used for any SQL statements(Select and Update both). | The executeQuery method can be used only with the select statement. | The executeUpdate method can be used to update/delete/insert operations in the database. |
| The execute method returns a boolean type value where true indicates that the ResultSet s returned which can later be extracted and false indicates that the integer or void value is returned. | The executeQuery() method returns a ResultSet object which contains the data retrieved by the select statement. | The executeUpdate() method returns an integer value representing the number of records affected where 0 indicates that query returns nothing. |
11) What are the different types of ResultSet?
ResultSet is categorized by the direction of the reading head and sensitivity or insensitivity of the result provided by it. There are three general types of ResultSet.| Type | Description |
| ResultSet.TYPE_Forward_ONLY | The cursor can move in the forward direction only. |
| ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE | The cursor can move in both the direction (forward and backward). The ResultSet is not sensitive to the changes made by the others to the database. |
| ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE | The cursor can move in both the direction. The ResultSet is sensitive to the changes made by the others to the database. |
12) What are the differences between ResultSet and RowSet?
| ResultSet | RowSet |
| ResultSet cannot be serialized as it maintains the connection with the database. | RowSet is disconnected from the database and can be serialized. |
| ResultSet object is not a JavaBean object | ResultSet Object is a JavaBean object. |
| ResultSet is returned by the executeQuery() method of Statement Interface. | Rowset Interface extends ResultSet Interface and returned by calling the RowSetProvider.newFactory().createJdbcRowSet() method. |
| ResultSet object is non-scrollable and non-updatable by default. | RowSet object is scrollable and updatable by default. |
13) How can we execute stored procedures using CallableStatement?
Following are the steps to create and execute stored procedures. Here, we are creating a table user420 by using a stored procedure and inserting values into it.- Create the procedure in the database. To call the stored procedure, you need to create it in the database. Here, we are assuming that the stored procedure looks like this.
- create or replace procedure "INSERTR"
- (id IN NUMBER,
- name IN VARCHAR2)
- is
- begin
- insert into user420 values(id,name);
- end;
- /
- create table user420(id number(10), name varchar2(200));
- Establish a network connection.
- Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(
- "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","oracle");
- Create the Object of CallableStatement.
- CallableStatement stmt=con.prepareCall("{call insertR(?,?)}");
- Provide the values and execute the query by using the following syntax.
- stmt.setInt(1,1011);
- stmt.setString(2,"Amit");
- stmt.execute();
- Check the database; the values will be found there. However, the complete code will look like the following.
- import java.sql.*;
- public class Proc {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
- Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(
- "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","oracle");
- CallableStatement stmt=con.prepareCall("{call insertR(?,?)}");
- stmt.setInt(1,1011);
- stmt.setString(2,"Amit");
- stmt.execute();
- System.out.println("success");
- }
- }
14) What is the role of the JDBC DriverManager class?
The DriverManager class acts as an interface between user and drivers. It keeps track of the drivers that are available and handles establishing a connection between a database and the appropriate driver. The DriverManager class maintains a list of Driver classes that have registered themselves by calling the method DriverManager.registerDriver().More details.
15) What are the functions of the JDBC Connection interface?
The Connection interface maintains a session with the database. It can be used for transaction management. It provides factory methods that return the instance of Statement, PreparedStatement, CallableStatement, and DatabaseMetaData.More details.
16) What does the JDBC ResultSet interface?
The ResultSet object represents a row of a table. It can be used to change the cursor pointer and get the information from the database. By default, ResultSet object can move in the forward direction only and is not updatable. However, we can make this object to move the forward and backward direction by passing either TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE or TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE in createStatement(int, int) method.More details.
17) What does the JDBC ResultSetMetaData interface?
The ResultSetMetaData interface returns the information of table such as the total number of columns, column name, column type, etc.More details.
18) What does the JDBC DatabaseMetaData interface?
The DatabaseMetaData interface returns the information of the database such as username, driver name, driver version, number of tables, number of views, etc. Consider the following example.- import java.sql.*;
- class Dbmd{
- public static void main(String args[]){
- try{
- Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(
- "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","oracle");
- DatabaseMetaData dbmd=con.getMetaData();
- System.out.println("Driver Name: "+dbmd.getDriverName());
- System.out.println("Driver Version: "+dbmd.getDriverVersion());
- System.out.println("UserName: "+dbmd.getUserName());
- System.out.println("Database Product Name: "+dbmd.getDatabaseProductName());
- System.out.println("Database Product Version: "+dbmd.getDatabaseProductVersion());
- con.close();
- }catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e);}
- }
- }
Driver Name: Oracle JDBC Driver Driver Version: 10.2.0.1.0XE Database Product Name: Oracle Database Product Version: Oracle Database 10g Express Edition Release 10.2.0.1.0 -Production
19) Which interface is responsible for transaction management in JDBC?
The Connection interface provides methods for transaction management such as commit(), rollback() etc.More details.
20) What is batch processing and how to perform batch processing in JDBC?
By using the batch processing technique in JDBC, we can execute multiple queries. It makes the performance fast. The java.sql.Statement and java.sql.PreparedStatement interfaces provide methods for batch processing. The batch processing in JDBC requires the following steps.- Load the driver class
- Create Connection
- Create Statement
- Add query in the batch
- Execute the Batch
- Close Connection
- import java.sql.*;
- class FetchRecords{
- public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
- Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","oracle");
- con.setAutoCommit(false);
- Statement stmt=con.createStatement();
- stmt.addBatch("insert into user420 values(190,'abhi',40000)");
- stmt.addBatch("insert into user420 values(191,'umesh',50000)");
- stmt.executeBatch();//executing the batch
- con.commit();
- con.close();
- }}
21) What are CLOB and BLOB data types in JDBC?
BLOB: Blob can be defined as the variable-length, binary large object which is used to hold the group of Binary data such as voice, images, and mixed media. It can hold up to 2GB data on MySQL database and 128 GB on Oracle database. BLOB is supported by many databases such as MySQL, Oracle, and DB2 to store the binary data (images, video, audio, and mixed media).CLOB: Clob can be defined as the variable-length, character-large object which is used to hold the character-based data such as files in many databases. It can hold up to 2 GB on MySQL database, and 128 GB on Oracle Database. A CLOB is considered as a character string.
22) What are the different types of lockings in JDBC?
A lock is a certain type of software mechanism by using which, we can restrict other users from using the data resource. There are four type of locks given in JDBC that are described below.- Row and Key Locks: These type of locks are used when we update the rows.
- Page Locks: These type of locks are applied to a page. They are used in the case, where a transaction remains in the process and is being updated, deleting, or inserting some data in a row of the table. The database server locks the entire page that contains the row. The page lock can be applied once by the database server.
- Table locks: Table locks are applied to the table. It can be applied in two ways, i.e., shared and exclusive. Shared lock lets the other transactions to read the table but not update it. However, The exclusive lock prevents others from reading and writing the table.
- Database locks: The Database lock is used to prevent the read and update access from other transactions when the database is open.
23) How can we store and retrieve images from the database?
By using the PreparedStatement interface, we can store and retrieve images. Create a table which contains two columns namely NAME and PHOTO.- CREATE TABLE "IMGTABLE"
- ( "NAME" VARCHAR2(4000),
- "PHOTO" BLOB
- )
- import java.sql.*;
- import java.io.*;
- public class InsertImage {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- try{
- Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(
- "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","oracle");
- PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement("insert into imgtable values(?,?)");
- ps.setString(1,"sonoo");
- FileInputStream fin=new FileInputStream("d:\\g.jpg");
- ps.setBinaryStream(2,fin,fin.available());
- int i=ps.executeUpdate();
- System.out.println(i+" records affected");
- con.close();
- }catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
- }
- }
- import java.sql.*;
- import java.io.*;
- public class RetrieveImage {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- try{
- Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(
- "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","oracle");
- PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement("select * from imgtable");
- ResultSet rs=ps.executeQuery();
- if(rs.next()){//now on 1st row
- Blob b=rs.getBlob(2);//2 means 2nd column data
- byte barr[]=b.getBytes(1,(int)b.length());//1 means first image
- FileOutputStream fout=new FileOutputStream("d:\\sonoo.jpg");
- fout.write(barr);
- fout.close();
- }//end of if
- System.out.println("ok");
- con.close();
- }catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace(); }
- }
- }
24) How can we store the file in the Oracle database?
The setCharacterStream() method of PreparedStatement interface is used to set character information into the parameterIndex. For storing the file into the database, CLOB (Character Large Object) datatype is used in the table. For example:- CREATE TABLE "FILETABLE"
- ( "ID" NUMBER,
- "NAME" CLOB
- )
- import java.io.*;
- import java.sql.*;
- public class StoreFile {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- try{
- Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(
- "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","oracle");
- PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement(
- "insert into filetable values(?,?)");
- File f=new File("d:\\myfile.txt");
- FileReader fr=new FileReader(f);
- ps.setInt(1,101);
- ps.setCharacterStream(2,fr,(int)f.length());
- int i=ps.executeUpdate();
- System.out.println(i+" records affected");
- con.close();
- }catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
- }
- }
25) How can we retrieve the file in the Oracle database?
The getClob() method of PreparedStatement is used to get file information from the database. Let's see the table structure of the example to retrieve the file.- CREATE TABLE "FILETABLE"
- ( "ID" NUMBER,
- "NAME" CLOB
- )
- import java.io.*;
- import java.sql.*;
- public class RetrieveFile {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- try{
- Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(
- "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","oracle");
- PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement("select * from filetable");
- ResultSet rs=ps.executeQuery();
- rs.next();//now on 1st row
- Clob c=rs.getClob(2);
- Reader r=c.getCharacterStream();
- FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("d:\\retrivefile.txt");
- int i;
- while((i=r.read())!=-1)
- fw.write((char)i);
- fw.close();
- con.close();
- System.out.println("success");
- }catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace(); }
- }
- }
26) What are the differences between stored procedure and functions?
The differences between stored procedures and functions are given below:| Stored Procedure | Function |
|---|---|
| Is used to perform business logic. | Is used to perform the calculation. |
| Must not have the return type. | Must have the return type. |
| May return 0 or more values. | May return only one value. |
| The procedure supports input and output parameters. | The function supports only input parameter. |
| Exception handling using try/catch block can be used in stored procedures. | Exception handling using try/catch can't be used in user-defined functions. |
27) How can we maintain the integrity of a database by using JDBC?
To maintain the integrity of a database, we need to ensure the ACID properties. ACID properties mean Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and durability. In JDBC, Connection interface provides methods like setAutoCommit(), commit(), and rollback() which can be used to manage transaction. Let's see an example of transaction management in JDBC.- import java.sql.*;
- class FetchRecords{
- public static void main(String args[])throws Exception{
- Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","oracle");
- con.setAutoCommit(false);
- Statement stmt=con.createStatement();
- stmt.executeUpdate("insert into user420 values(190,'abhi',40000)");
- stmt.executeUpdate("insert into user420 values(191,'umesh',50000)");
- con.commit();
- con.close();
- }}
28) What is the JDBC Rowset?
JDBC Rowset is the wrapper of ResultSet. It holds tabular data like ResultSet, but it is easy and flexible to use. The implementation classes of RowSet interface are as follows:- JdbcRowSet
- CachedRowSet
- WebRowSet
- JoinRowSet
- FilteredRowSet
29) What is the major difference between java.util.Date and java.sql.Date data type?
The major difference between java.util.Date and java.sql.Date is that, java.sql.Date represents date without time information whereas, java.util.Date represents both date and time information.30) What does JDBC setMaxRows method do?
The setMaxRows(int i) method limits the number of rows the database can return by using the query. This can also be done within the query as we can use the limit cause in MySQL.
No comments:
Post a Comment